Arrays in C++
Arrays
An array is defined as a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations under the same name. Ex: int (a,b,c,d,e ) can be grouped in a single variable as int a[5]. Now five continuous memory location are assigned with the same name ‘a’. Instead of creating separate variables to store data, it is an efficient organization to store data in a single variable called array.

Basic properties of Array
- Array index always starts with zero and ends with n-1 (n is the size)
ex:int a[5] has the index range a[0],a[1],….a[4] - An array is homogeneous: It stores elements of the same type only.
ex: int a[5], integer array stores only integer elements.
Ways to define an array
Array definition by specifying the size
int a[5];
As per C99 versions, we can also declare an array of user-specified size
int n = 5;
int a[n];
Array definition by initializing elements
int a[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40,50 } ;Here size corresponds to the number of elements initialized, hence size = 4.
Array definition by specifying size and initializing
int a[5] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 ,50}; 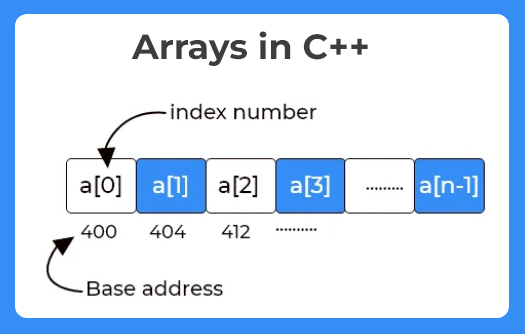
Initializing and accessing 1D array
#include < iostream >
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={6,9,1,5,3};//direct declartion and initialisation
cout<<"elements are:\n";
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)// iterate all the elements
cout<<"a["<<i<<"]="<<a[i]<<"\n";//access though index
return 0;
}
Output:
elements are: a[0]=6 a[1]=9 a[2]=1 a[3]=5 a[4]=3
Advantages
- Reduces program size
- Reduces access time
- Efficient data organization
Disadvantages
Array size is static, due to which there may be chances of wastage and shortage of memory
Array elements are addressed sequentially
- The address of each block will be sequentially located to access the memory blocks by using pointers.
- Generally, normal user access the array data with subscripted index i.e. a[n] internally compiler will access by address and pointers.
From the below example it is clear that a[0] is stored at location 0x6ff20 ,as it is an integer array element takes 4 bytes i.e. a[1] at address 0x6ff24 and a[2] at address 0x6ff28 and so on
Example:-
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={6,9,1,5,3};
cout<<"elements are:\n";
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
cout<<"a["<<&a[i]<<"]="<<a[i]<<"\n";
return 0;
}
Output:
elements are: a[0x6ff20]=6 a[0x6ff24]=9 a[0x6ff28]=1 a[0x6ff32]=5 a[0x6ff36]=3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "how many elements?:"; cin >> n;int a[n], count = 0, key;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i];
}
cout << "enter an element to find its frequency:"; cin >> key;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] == key)
count++;
}
cout << "frequency of b "<< count;
return 0;
}
Output
how many elements?:6 2 3 4 4 5 6 enter an element to find its frequency:4 frequency of 4 is 2 enter an element to find its frequency:3 frequency of 3 is 1 enter an element to find its frequency:9 frequency of 4 is 0
Additions Facts about Arrays
An array index cannot be negative or zero
a[-2];//invalid
a[0];//invalid
Unused space in the array is always filled with zeros
int a[5]={1,2,3};//a[3],a[4] are filled with zerosAll array elements are Garbage values before initialization of values
int a[5];//a[0]...a[5] are garbage valuesDeclaring an array without size is invalid
int a[];/invalidThe below array declaration sets all elements in the array to 0
int a[10]={0}; 2D Arrays
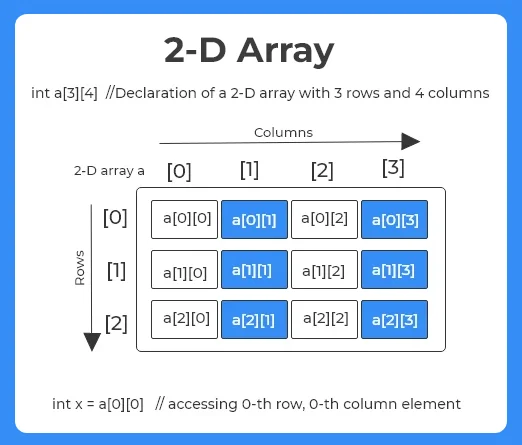
- Two-dimensional arrays are represented using two indexes namely row and column
- A 2D array is viewed as an array of arrays.
Size of multidimensional arrays
- Total number of elements that can be stored in a multidimensional array can be calculated by multiplying the number of rows and columns.
For example:
- The array int a[3][3] can store total (3*3) = 9 elements.
- Similarly array int a[2][3] can store total (2*3) = 6 elements.
Defining 2D array
data_type name[rows][columums];
ex: int a[3][3];
Initializing Two – Dimensional Arrays:
First way:
int a[3][3] = {0, 1 ,2 ,3 ,4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 };The elements will be filled in the array in the order, first 3 elements from the left in the first row, next 3 elements in the second row and so on.
Second way:
int a[3][3] = {{0,1,2}, {3,4,5,}, {6,7,8}};- This type of initialization makes use of nested braces. Each set of inner braces represents one row.
- In the above example, there are total of three rows so there are three sets of inner braces.
Accessing 2D Arrays
Elements in two-dimensional arrays are commonly referred by a[i][j] where i is the row number and ‘j’ is the column number.
example:
a[2][1];
- a[2][1] element is located at index 2nd row and 1st column
- A two – dimensional array can be seen as a table with ‘m’ rows and ‘n’ columns where the row number ranges from 0 to (m-1)
example: array a[3][3] ranges from i.e a[0][0] to a[2][2]
C++ program to initialise and access a 2D array
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// an array with 5 rows and 2 columns.
int a[5][2] = { {0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6},{4,8}};
for ( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ )//iterate rows
for ( int j = 0; j < 2; j++ ) //iterate columns
{
cout << "a[" << i << "][" << j << "]: ";
cout << a[i][j]<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
a[0][0]: 0 a[0][1]: 0 a[1][0]: 1 a[1][1]: 2 a[2][0]: 2 a[2][1]: 4 a[3][0]: 3 a[3][1]: 6 a[4][0]: 4 a[4][1]: 8
Advantage of Multidimensional arrays
Access time is reduced as search confines only to that particular row.
ex: to access a[3][2] search starts directly from row index 2 rather than starting from index 0 as in the case of the 1D array.
Conclusion
In conclusion, arrays are a powerful tool in C++ programming, allowing developers to efficiently manage collections of data. Understanding how to declare, initialize, and manipulate arrays is crucial for writing effective and bug-free C++ code. As you continue your programming journey, mastering arrays will open doors to more complex data structures and algorithms.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment