Verbal Menu
- Basic Grammar
- Speech and Voices
- Tenses
- Articles
- Tenses and Articles
- Idioms and Phrases
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Prepositions and Conjunction
- Selecting Words
- Relative Pronoun
- Sentence Completion
- Sentence Ordering
- Contextual Vocabulary
- Jumbled Sentence
- Sentence Formation
- Error Identification
- Sentence Improvement and Construction
- Cloze Test
- Fill in the blanks
- Paragraph Ordering
- Para Jumbles
- Synonyms and Antonyms
- Synonyms
- Antonyms
- Reading Comprehension
- Get Off-campus Drive Updates
- Get Hiring Updates
- Contact US
PREPINSTA PRIME
Tips And Tricks And Shortcuts For Sentence Formation
Sentence Formation Tips and Tricks and Shortcuts:
The Tips and Tricks and Shortcuts for Sentence Formation may take some time to understand but it is important that one learns how to write or form short and meaningful sentences.
On a basic level, most English sentences follow a similar structure. Here are a few tips to make constructing English sentences easy.
Every word in a sentence serves a specific purpose within the structure of that particular sentence. So without omitting the required information, you should know to form sentences that are grammatically accurate.
Sentence Formation Tips and Tricks and Shortcuts
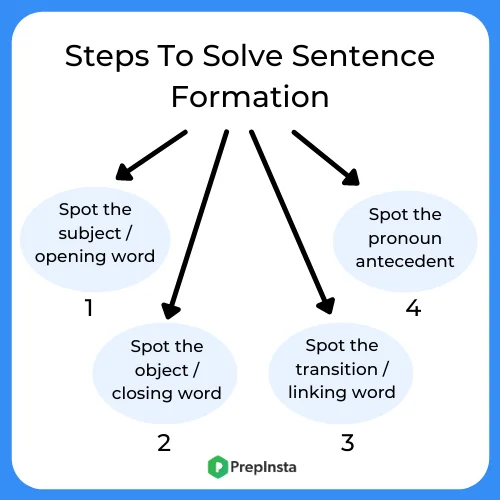
1. Spotting the Subject or the opening word:
- The first and foremost step in addressing such problems is to identify the opening word.
- For that one has to go through all the scattered words mentioned in the options, then try to get an overall idea behind the sentence, and if we get that, then it will become effortless to perform the remaining task.
2. Identify the object or the closing part of the sentence:
- The next step is to figure out the closing word of the sentence.
- Which again requires reading all the words that are mentioned in the options, and accordingly try to co-relate it with the subject/introductory word and the remaining other words hat will eventually form the sentence
3. Spotting the transition words or the linking words:
The next step is to identify the transition words which entail the shifting from one idea to another. Some of the frequently used transition words are:
4. Identifying the pronoun antecedents:
- The last step is to spot the pronouns used in the sentence. Here again, the pronouns can be categorized into three types, namely
- Relative pronoun: Which consists of words like who, whom, whose, which.
- Demonstrative pronoun: It mainly consists of words like this, that, these, those.
- Personal pronoun: Personal pronoun consists of words like he, she, him, her, you, they, it.
After identifying these pronouns, scan all the options, and try to set a connection between all the words coherently and logically.
Note: The above tips are applicable in the case of complex or compound sentences.
- It is not essential that each sentence must contain the transition words or the pronoun antecedents.
- There might be many questions where we shall be asked to create a simple sentence. (This can be depicted easily by looking at the options)
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Tips and Tricks and Shortcuts for Sentence
Formation - Practice Questions
Type 1: Simple Sentences
Also known as independent sentences, these sentences maintain their individuality, as they do not have any dependent clause.
It is better explained with the help of an example below:
Question 1:
The below-mentioned sentence is broken into 4-5 parts, Join these parts to make a meaningful sentence.
- Everyone
- Heard
- Of
- Her
- Had
Options:
A. 15234
B. 42351
C. 15432
D. 15342
Correct option: A
Explanation:
The correct way to write the sentence is:
“Everyone had heard of her.”
Type 2: Compound sentence
This sentence, unlike simple sentences, consists of two independent clauses.
Simply put, a compound sentence is a combination of two individual clauses that are blended perfectly (With the help of a transition word) to derive a meaningful sentence that makes sense.
Here the quick tip to identify a compound is to memorize the FANBOYS acronym which stands for:
F – for
A-and
N- nor
B- but
O- or
Y- yet
S- So
Now if we find any sentence that contains any one of the above words, then that sentence will definitely be a compound sentence.
It is better explained with the help of an example below:
Question 1:
The below-mentioned sentence is broken into 4-5 parts, Join these parts to make a meaningful sentence.
- girls
- boys
- Grown-up
- and
- need to
- Instructed every time.
- be
- do not
Options:
A. 43217586
B. 31428576
C. 52143786
D. None of the above
Correct option: B
Explanation:
The correct form of writing the above sentence is:
Grown-up girls and boys do not need to be instructed every time.
Question: 2
- I
- running
- and
- like
- I
- like
- Swimming
Options:
- 1473562
- 2345671
- 7653241
- None of the above
Correct option: A
Explanation:
The correct form of writing the above sentence is:
I lie swimming and I like running.
Type 3: Complex sentences
Complex sentences, unlike compound sentences, have one or more than one clause. While most of the clauses are dependent, however, it might contain some independent clauses.
We can easily trace out the dependent clause by locating the above-mentioned transition words (if, when, before to name a few)
Their one type is mentioned in the example below:
Question 1:
The below-mentioned sentence is broken into 4-5 parts, Join these parts to make a meaningful sentence.
- no snowfall
- There
- until
- would be
- December.
Options:
A. 24135
B. 12435
C. 24135
D. 42135
Correct option: A
Explanation:
The correct formation of the sentence is mentioned below:
“There would be no snowfall until December.”
Question: 2
- Was considered
- her exams.
- she
- Failed
- Smart,
- She
- Although
- All
Options:
- 7315642
- 67543218
- 73165428
- None of the above
Correct Option: B
Explanation:
The correct form of writing the above sentence is:
Although she was considered smart, she failed all her exams.
Also Check Out
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
- Sentence Ordering – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Contextual Vocabulary – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Jumbled Sentence – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Error Identification – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Sentence Improvement and Construction – Questions | Rules | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Sentence Ordering – Questions |
Rules |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Contextual Vocabulary –
Questions |
Rules |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Jumbled Sentence – Questions |
Rules |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Error Identification – Questions |
Rules |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Sentence Improvement and Construction – Questions |
Rules |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates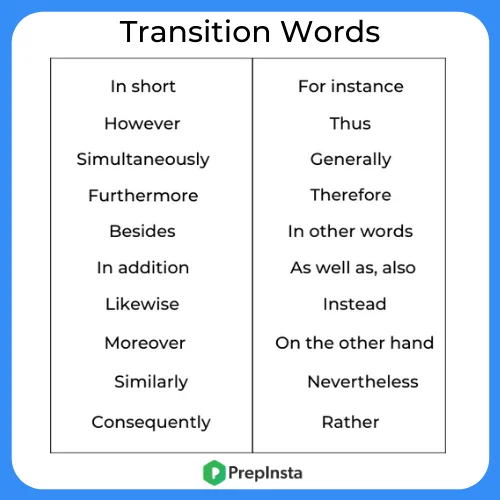





Login/Signup to comment