Quants Menu
- HCF and LCM
- Number System
- Number Decimals & Fractions
- Surds and Indices
- Divisibility
- Ages
- LCM
- HCF
- Inverse
- Speed Time and Distance
- Work and Time
- Boats and Streams
- Pipes and Cisterns
- Averages
- Allegations and Mixtures
- Ratio and Proportions
- Simple & Compound Interest
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Percentages
- Profit & Loss
- Successive Discount 1
- Successive Discount 2
- AP GP HP
- Arithmetic Progressions
- Geometric Progressions
- Harmonic Progressions
- Probability
- Permutation & Combination
- Combination
- Circular Permutation
- Geometry
- Heights and Distances
- Perimeter Area and Volume
- Coordinate Geometry
- Venn Diagrams
- Set Theory
- Algebra
- Linear Equations
- Quadratic Equations
- Logarithms
- Clocks
- Calendars
- Clocks and Calendars
- Finding remainder of large powers
PREPINSTA PRIME
Formulas for Coordinate Geometry
Coordinate Geometry Formulas
Co-ordinate geometry is considered as one of the most easiest chapters from Quantitative Aptitude Section which can be asked in an Exam. This page here will give you all the required Formulas for Coordinate Geometry.
So that you can ace the questions asked from this chapter in any of the exams you wish to appear.
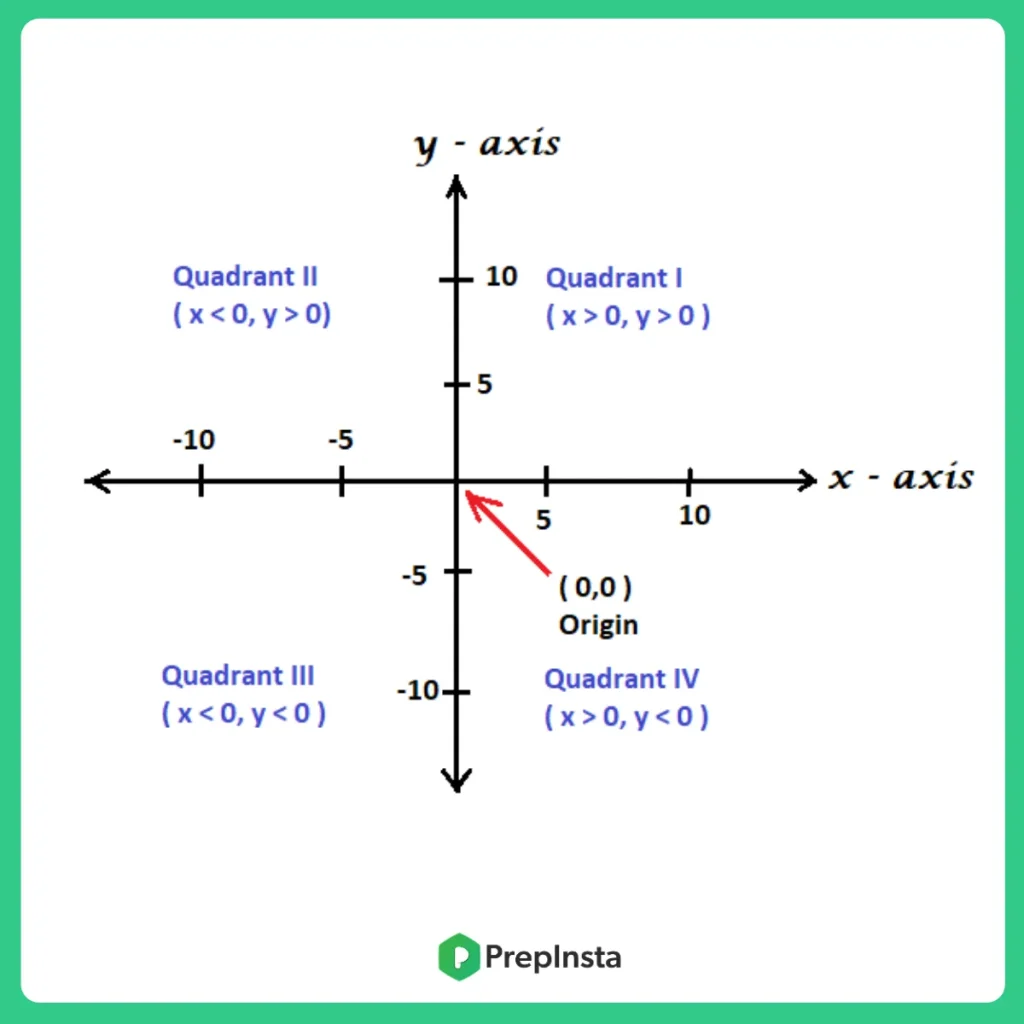
What is Coordinate Geometry?
- Coordinate geometry is a branch of geometry where the position of the points on the plane is defined with the help of an ordered pair of numbers also known as coordinates.
Coordinate Geometry Formulas and Basic Concept
- The point of intersection of the x and the y-axis is known as the origin. At this point, both x and y are 0.
- The values on the right-hand side of the x-axis are positive and the values on the left-hand side of the x-axis are negative.
- Similarly, on the y-axis, the values located above the origin are positive and the values located below the origin are negative.
Formulas Required for Solving Coordinate Geometry Questions.
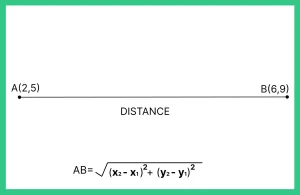
- Distance between two points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2)
AB = [latex]\sqrt{(x_{2}- x_{1})^2 + (y_{2}- y_{1})^2}[/latex]
- Slope of line when two points are given (x1, y1) and (x2, y2)
m = [latex]\frac{(y_{1}- y_{2})}{(x_{1}- x_{2})}[/latex]
- Slope of line when linear equation is given ax + by = c => [latex] – \frac{a}{b}[/latex]
- Midpoint =[latex]\frac{x_{1} + x_{2}}{2},\frac{y_{1} + y_{2}}{2}[/latex]
- The co-ordinates of a point R(x,y) that divides a line segment joining two points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) internally in the ratio m:n is given by
x = [latex]\frac{ m x_{2} + nx_{1}}{m + n}[/latex]
y = [latex]\frac{my_{2} + ny_{1} }{m + n}[/latex]
- The co-ordinates of a point R(x,y) that divides a line segment joining two points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) externally in the ratio m:n is given by
x =[latex]\frac{ m x_{2} – nx_{1}}{m – n}[/latex]
y = [latex]\frac{my_{2} – ny_{1} }{m – n}[/latex]
- Centroid of a triangle with its vertices (x1,y1), (x2,y2), (x3,y3)
C = [latex]\frac{x_{1}+ x_{2} + x_{3}}{3}[/latex], [latex]\frac{y_{1}+ y_{2} + y_{3}}{3}[/latex]
- Area of a Triangle with its vertices A(x1,y1), B(x2,y2), C(x3,y3)
A =[latex]\frac{1}{2} ×[ (x_{1}(y_{2}-y_{3}) + (x_{2}(y_{3}-y_{1}) ) + (x_{3}(y_{1}-y_{2}) )][/latex]
- Division of a line segment by a point
If a point p(x, y) divides the join of A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2), in the ratio m: n, then
x= [latex]\frac{ m x_{2} + nx_{1}}{m + n}[/latex] and y= [latex]\frac{my_{2} + ny_{1} }{m + n}[/latex]
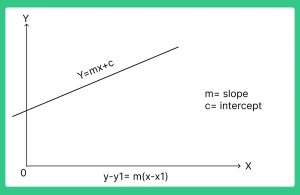
- The equation of a line in slope intercept form is Y= mx+ c, where m is its slope.
The equation of a line which has gradient m and which passes through the point (x1, y1) is =
y – y1 = m(x – x1).
Some Examples Using Above Formulas:
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Question 1: Given two points A(2, 5) and B(6, 9), find the Distance between points A(2, 5) and B(6, 9)
Answer: Distance between points A(2, 5) and B(6, 9):
Distance = [latex]\sqrt{6-2}^{2}[/latex]+[latex]\sqrt{9-5}^{2}[/latex]
=[latex]\sqrt{4^{2}+4^{2}}[/latex] =
[latex]\sqrt{32}[/latex] =
5.66 Ans
Question 2:If the slope of a line is -2/3 and it passes through the point (2, 5), find the equation of the line in point-slope form.
Answer: Equation of the line passing through points P(3, 8) and Q(5, -2):
Slope (m) =[latex]\frac{change in y}{change in x}[/latex] =[latex]\frac{-2-8}{5-3}[/latex]=[latex]\frac{-10}{2}[/latex]=-5
Using the point-slope form: y – y1 = m(x – x1)
y – 8 = -5(x – 3)
y – 8 = -5x + 15
y = -5x + 23
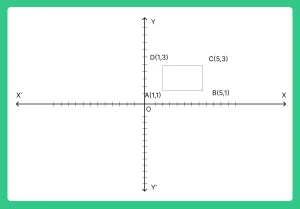
Area = Length * Width Length =
Distance between points B and C:
Length = √((5 – 5)^2 + (3 – 1)^2) = √(0 + 4) = √4 = 2
Width = Distance between points A and B:
Width = √((5 – 1)^2 + (1 – 1)^2) = √(16 + 0) = √16 = 4 Area = 2 * 4 = 8 square units
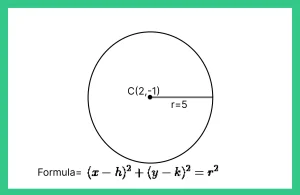
The equation of a circle with center (h, k) and radius r is [latex](x-h)^{2} + (y-k)^{2} = r^{2}[/latex]
For this circle: = [latex](x-h)^{2} + (y-(-1)^{2}[/latex] = [latex]r^{2}[/latex]=[latex]5^2 (x – 2)^2 + (y + 1)^2[/latex] = 25
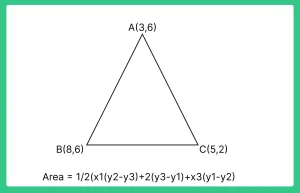
Answer: Area of triangle ABC with vertices A(3, 6), B(8, 6), and C(5, 2):
Area = ½ |x1(y2 – y3) + x2(y3 – y1) + x3(y1 – y2)|
Area = ½ |3(6 – 2) + 8(2 – 6) + 5(6 – 6)|
Area = ½ |12 – 24 + 0|
Area = ½ |-12|
Area = 6 square units
Also Check Out
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
- Geometry – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Heights and Distances – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Perimeter Area and Volume – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Venn Diagrams – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Set Theory – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Geometry – Questions |
Formulas |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Heights and Distances – Questions |
Formulas |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Perimeter Area and Volume – Questions |
Formulas |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Venn Diagrams – Questions |
Formulas |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts - Set Theory – Questions |
Formulas |
How to Solve Quickly |
Tricks & Shortcuts

 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates




Login/Signup to comment