TCS Digital Interview Questions and Answers
TCS Digital Interview Questions for Freshers 2023
Find all the information regarding TCS Digital Interview Questions and TCS Digital Interview Experience, including the interview patterns and most asked interview questions.
Page Highlights:
- TCS Digital Interview Pattern
- TCS Digital Interview Questions

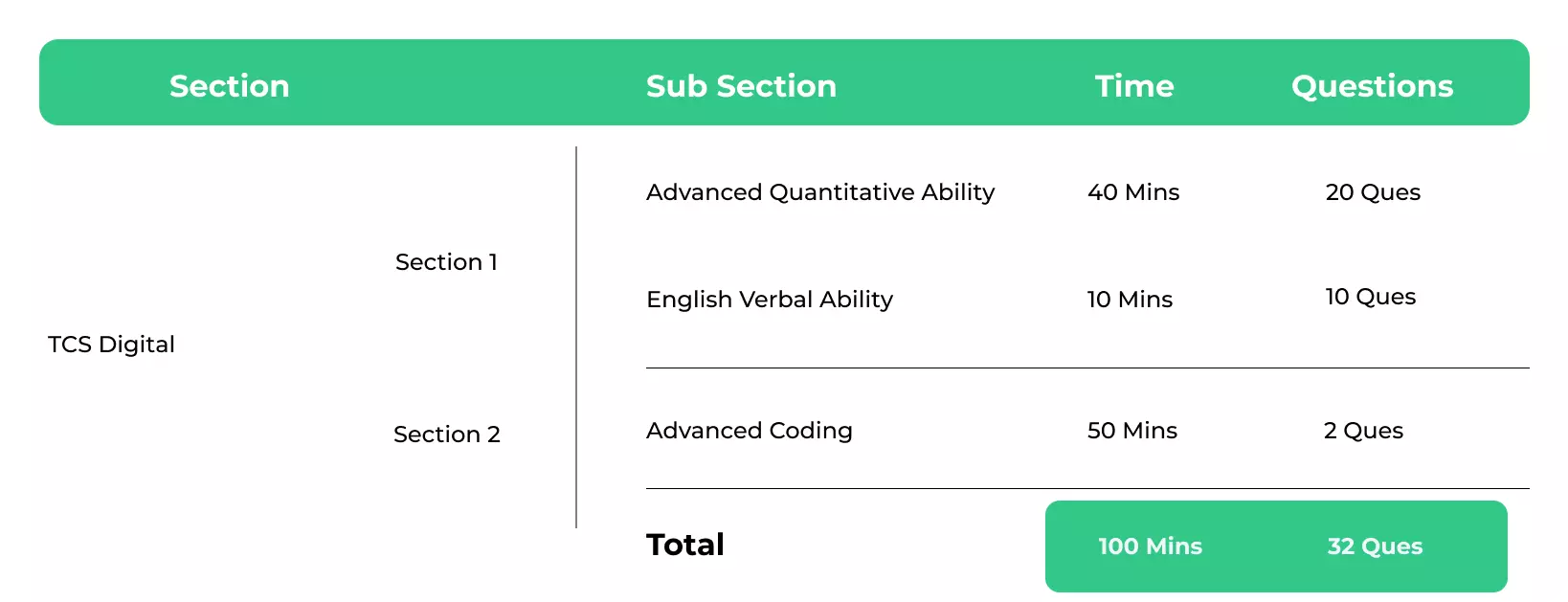
TCS Digital Interview Pattern
TCS conducts three interview rounds, which includes:-
- TCS Technical Interview
- TCS MR Interview
- TCS HR Interview
TCS conducts 3 interviews either on the same day or within a span of two days. Interview Questions for TCS Digital include programming questions and computer fundamentals.
Most Asked Topics in TCS Digital Interview:-
- Programming Questions ( C, JAVA, Python, C++)
- OOPS concepts
- DBMS
- DSA
- Operating Systems
- Recent Technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Big Data etc
Use Coupon Code “CT10” and get flat 10% OFF on your Prime Subscription :
- 1 month extra subscription on 3 & 6 months plans
- 2 months extra subscription on 12 & 24 months plans
- 3 months extra subscription on 36 & 48 months plan
TCS Digital Interview Technical Questions
Q1. What is Cloud Computing?
It is advance stage technology implemented so that the cloud provides the services globally as per the user requirements. It provides a method to access several servers worldwide.
Q2. What are the benefits of cloud computing?
The main benefits of cloud computing are:
- Data backup and storage of data
- Powerful server capabilities.
- Incremented productivity.
- Cost effective and time saving.
Companies like Amazon which owns AWS, Microsoft which owns Azure, VMware which provides cloud desktop. Google which provides various cloud solutions like Google Drive, Slides/Docs/ Google Cloud platform etc are example of such.
Q3. What are the Cloud Service Models?
- Infrastructure as a service
- (IaaS) Platform as a service
- (PaaS) Software as a service (SaaS)
Q4. What is Digital Technology?
When TCS will come to your campus they will have a presentation about TCS Digital. According to TCS Digital Technology are the blend of these five –
- Data
- Cloud
- Intelligence
- Inter connectivity
- Visual Computing
This information they will cover in the presentation.
Note:-It was seen in VIT, Vellore where TCS asked this question in the presentation open to all and the student who answered it was directly called for interview and was asked to skip the Online test.
When TCS will come to your campus they will have a presentation about TCS Digital. According to TCS Digital Technology are the blend of these five –
This information they will cover in the presentation.
Note:-It was seen in VIT, Vellore where TCS asked this question in the presentation open to all and the student who answered it was directly called for interview and was asked to skip the Online test.
Q5. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) makes it possible for machines to learn from experience, adjust to new inputs and perform human-like tasks. Most AI examples that you hear about today – from chess-playing computers to self-driving cars – rely heavily on deep learning and natural language processing. Using these technologies, computers can be trained to accomplish specific tasks by processing large amounts of data and recognizing patterns in the data.
Q6. Why is artificial intelligence important?
- AI automates repetitive learning and discovery through data. But AI is different from hardware-driven, robotic automation. Instead of automating manual tasks, AI performs frequent, high-volume, computerized tasks reliably and without fatigue. For this type of automation, human inquiry is still essential to set up the system and ask the right questions.
- AI adds intelligence to existing products. In most cases, AI will not be sold as an individual application. Rather, products you already use will be improved with AI capabilities, much like Siri was added as a feature to a new generation of Apple products. Automation, conversational platforms, bots and smart machines can be combined with large amounts of data to improve many technologies at home and in the workplace, from security intelligence to investment analysis.
- AI adapts through progressive learning algorithms to let the data do the programming. AI finds structure and regularities in data so that the algorithm acquires a skill: The algorithm becomes a classifier or a predicator. So, just as the algorithm can teach itself how to play chess, it can teach itself what product to recommend next online. And the models adapt when given new data. Back propagation is an AI technique that allows the model to adjust, through training and added data, when the first answer is not quite right.
- AI analyzes more and deeper data using neural networks that have many hidden layers. Building a fraud detection system with five hidden layers was almost impossible a few years ago. All that has changed with incredible computer power and big data. You need lots of data to train deep learning models because they learn directly from the data. The more data you can feed them, the more accurate they become.
- AI achieves incredible accuracy though deep neural networks – which was previously impossible. For example, your interactions with Alexa, Google Search and Google Photos are all based on deep learning – and they keep getting more accurate the more we use them. In the medical field, AI techniques from deep learning, image classification and object recognition can now be used to find cancer on MRIs with the same accuracy as highly trained radiologists.
- AI automates repetitive learning and discovery through data. But AI is different from hardware-driven, robotic automation. Instead of automating manual tasks, AI performs frequent, high-volume, computerized tasks reliably and without fatigue. For this type of automation, human inquiry is still essential to set up the system and ask the right questions.
- AI adds intelligence to existing products. In most cases, AI will not be sold as an individual application. Rather, products you already use will be improved with AI capabilities, much like Siri was added as a feature to a new generation of Apple products. Automation, conversational platforms, bots and smart machines can be combined with large amounts of data to improve many technologies at home and in the workplace, from security intelligence to investment analysis.
- AI adapts through progressive learning algorithms to let the data do the programming. AI finds structure and regularities in data so that the algorithm acquires a skill: The algorithm becomes a classifier or a predicator. So, just as the algorithm can teach itself how to play chess, it can teach itself what product to recommend next online. And the models adapt when given new data. Back propagation is an AI technique that allows the model to adjust, through training and added data, when the first answer is not quite right.
- AI analyzes more and deeper data using neural networks that have many hidden layers. Building a fraud detection system with five hidden layers was almost impossible a few years ago. All that has changed with incredible computer power and big data. You need lots of data to train deep learning models because they learn directly from the data. The more data you can feed them, the more accurate they become.
- AI achieves incredible accuracy though deep neural networks – which was previously impossible. For example, your interactions with Alexa, Google Search and Google Photos are all based on deep learning – and they keep getting more accurate the more we use them. In the medical field, AI techniques from deep learning, image classification and object recognition can now be used to find cancer on MRIs with the same accuracy as highly trained radiologists.
Q7. What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is an application of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides systems the ability to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning focuses on the development of computer programs that can access data and use it learn for themselves.
The process of learning begins with observations or data, such as examples, direct experience, or instruction, in order to look for patterns in data and make better decisions in the future based on the examples that we provide. The primary aim is to allow the computers learn automatically without human intervention or assistance and adjust actions accordingly.
The process of learning begins with observations or data, such as examples, direct experience, or instruction, in order to look for patterns in data and make better decisions in the future based on the examples that we provide. The primary aim is to allow the computers learn automatically without human intervention or assistance and adjust actions accordingly.
Q8. What is Big Data?
Big data is a term that describes the large volume of data – both structured and unstructured – that inundates a business on a day-to-day basis. But it’s not the amount of data that’s important. It’s what organizations do with the data that matters. Big data can be analyzed for insights that lead to better decisions and strategic business moves.
Q9. Why Is Big Data Important?
The importance of big data doesn’t revolve around how much data you have, but what you do with it. You can take data from any source and analyze it to find answers that enable
- cost reductions
- time reductions
- new product development
- optimized offerings
- smart decision making.
When you combine big data with high-powered analytics, you can accomplish business-related tasks such as:
- Determining root causes of failures, issues and defects in near-real time.
- Generating coupons at the point of sale based on the customer’s buying habits.
- Recalculating entire risk portfolios in minutes.
- Detecting fraudulent behavior before it affects your organization.
The importance of big data doesn’t revolve around how much data you have, but what you do with it. You can take data from any source and analyze it to find answers that enable
- cost reductions
- time reductions
- new product development
- optimized offerings
- smart decision making.
When you combine big data with high-powered analytics, you can accomplish business-related tasks such as:
- Determining root causes of failures, issues and defects in near-real time.
- Generating coupons at the point of sale based on the customer’s buying habits.
- Recalculating entire risk portfolios in minutes.
- Detecting fraudulent behavior before it affects your organization.
Q 10. What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a machine learning technique that teaches computers to do what comes naturally to humans: learn by example. Deep learning is a key technology behind driverless cars, enabling them to recognize a stop sign, or to distinguish a pedestrian from a lamppost. It is the key to voice control in consumer devices like phones, tablets, TVs, and hands-free speakers. Deep learning is getting lots of attention lately and for good reason. It’s achieving results that were not possible before.
Deep learning is a machine learning technique that teaches computers to do what comes naturally to humans: learn by example. Deep learning is a key technology behind driverless cars, enabling them to recognize a stop sign, or to distinguish a pedestrian from a lamppost. It is the key to voice control in consumer devices like phones, tablets, TVs, and hands-free speakers. Deep learning is getting lots of attention lately and for good reason. It’s achieving results that were not possible before.
Q 11. What is cyber security?
Cybersecurity is the protection of internet-connected systems, including hardware, software and data, from cyberattacks.
In a computing context, security comprises cybersecurity and physical security — both are used by enterprises to protect against unauthorized access to data centers and other computerized systems. Information security, which is designed to maintain the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data, is a subset of cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is the protection of internet-connected systems, including hardware, software and data, from cyberattacks.
In a computing context, security comprises cybersecurity and physical security — both are used by enterprises to protect against unauthorized access to data centers and other computerized systems. Information security, which is designed to maintain the confidentiality, integrity and availability of data, is a subset of cybersecurity.
Q 12. What are the different types of cyber-attacks?
Malware
- If you’ve ever seen an antivirus alert pop up on your screen, or if you’ve mistakenly clicked a malicious email attachment, then you’ve had a close call with malware. Attackers love to use malware to gain a foothold in users’ computers—and, consequently, the offices they work in—because it can be so effective.
- “Malware” refers to various forms of harmful software, such as viruses and ransomware. Once malware is in your computer, it can wreak all sorts of havoc, from taking control of your machine, to monitoring your actions and keystrokes, to silently sending all sorts of confidential data from your computer or network to the attacker’s home base.
- Attackers will use a variety of methods to get malware into your computer, but at some stage it often requires the user to take an action to install the malware. This can include clicking a link to download a file, or opening an attachment that may look harmless (like a Word document or PDF attachment), but actually has a malware installer hidden within.
Phishing
- Of course, chances are you wouldn’t just open a random attachment or click on a link in any email that comes your way—there has to be a compelling reason for you to take action. Attackers know this, too. When an attacker wants you to install malware or divulge sensitive information, they often turn to phishing tactics, or pretending to be someone or something else to get you to take an action you normally wouldn’t. Since they rely on human curiosity and impulses, phishing attacks can be difficult to stop.
- In a phishing attack, an attacker may send you an email that appears to be from someone you trust, like your boss or a company you do business with. The email will seem legitimate, and it will have some urgency to it (e.g. fraudulent activity has been detected on your account). In the email, there will be an attachment to open or a link to click. Upon opening the malicious attachment, you’ll thereby install malware in your computer. If you click the link, it may send you to a legitimate-looking website that asks for you to log in to access an important file—except the website is actually a trap used to capture your credentials when you try to log in.
- In order to combat phishing attempts, understanding the importance of verifying email senders and attachments/links is essential.
SQL Injection Attack
- SQL (pronounced “sequel”) stands for structured query language; it’s a programming language used to communicate with databases. Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases. A SQL injection attack specifically targets this kind of server, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally wouldn’t. This is especially problematic if the server stores private customer information from the website, such as credit card numbers, usernames and passwords (credentials), or other personally identifiable information, which are tempting and lucrative targets for an attacker.
- An SQL injection attack works by exploiting any one of the known SQL vulnerabilities that allow the SQL server to run malicious code. For example, if a SQL server is vulnerable to an injection attack, it may be possible for an attacker to go to a website’s search box and type in code that would force the site’s SQL server to dump all of its stored usernames and passwords for the site.
Malware
- If you’ve ever seen an antivirus alert pop up on your screen, or if you’ve mistakenly clicked a malicious email attachment, then you’ve had a close call with malware. Attackers love to use malware to gain a foothold in users’ computers—and, consequently, the offices they work in—because it can be so effective.
- “Malware” refers to various forms of harmful software, such as viruses and ransomeware. Once malware is in your computer, it can wreak all sorts of havoc, from taking control of your machine, to monitoring your actions and keystrokes, to silently sending all sorts of confidential data from your computer or network to the attacker’s home base.
- Attackers will use a variety of methods to get malware into your computer, but at some stage it often requires the user to take an action to install the malware. This can include clicking a link to download a file, or opening an attachment that may look harmless (like a Word document or PDF attachment), but actually has a malware installer hidden within.
Phishing
- Of course, chances are you wouldn’t just open a random attachment or click on a link in any email that comes your way—there has to be a compelling reason for you to take action. Attackers know this, too. When an attacker wants you to install malware or divulge sensitive information, they often turn to phishing tactics, or pretending to be someone or something else to get you to take an action you normally wouldn’t. Since they rely on human curiosity and impulses, phishing attacks can be difficult to stop.
- In a phishing attack, an attacker may send you an email that appears to be from someone you trust, like your boss or a company you do business with. The email will seem legitimate, and it will have some urgency to it (e.g. fraudulent activity has been detected on your account). In the email, there will be an attachment to open or a link to click. Upon opening the malicious attachment, you’ll thereby install malware in your computer. If you click the link, it may send you to a legitimate-looking website that asks for you to log in to access an important file—except the website is actually a trap used to capture your credentials when you try to log in.
- In order to combat phishing attempts, understanding the importance of verifying email senders and attachments/links is essential.
SQL Injection Attack
- SQL (pronounced “sequel”) stands for structured query language; it’s a programming language used to communicate with databases. Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases. A SQL injection attack specifically targets this kind of server, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally wouldn’t. This is especially problematic if the server stores private customer information from the website, such as credit card numbers, usernames and passwords (credentials), or other personally identifiable information, which are tempting and lucrative targets for an attacker.
- An SQL injection attack works by exploiting any one of the known SQL vulnerabilities that allow the SQL server to run malicious code. For example, if a SQL server is vulnerable to an injection attack, it may be possible for an attacker to go to a website’s search box and type in code that would force the site’s SQL server to dump all of its stored usernames and passwords for the site.
Q 13. What is IOT i.e. Internet of Things?
Internet of Things (IoT) is an ecosystem of connected physical objects that are accessible through the internet. The ‘thing’ in IoT could be a person with a heart monitor or an automobile with built-in-sensors, i.e. objects that have been assigned an IP address and have the ability to collect and transfer data over a network without manual assistance or intervention. The embedded technology in the objects helps them to interact with internal states or the external environment, which in turn affects the decisions taken.
Applications include –
- Smart homes
- Wearable (Smart watches)
- Manufacturing Industries’
- Transportation
- Agriculture
- Retail Industries
- Healthcare etc.
Internet of Things (IoT) is an ecosystem of connected physical objects that are accessible through the internet. The ‘thing’ in IoT could be a person with a heart monitor or an automobile with built-in-sensors, i.e. objects that have been assigned an IP address and have the ability to collect and transfer data over a network without manual assistance or intervention. The embedded technology in the objects helps them to interact with internal states or the external environment, which in turn affects the decisions taken. Applications include –
- Smart homes
- Wearable (Smart watches)
- Manufacturing Industries’
- Transportation
- Agriculture
- Retail Industries
- Healthcare etc.
Q 14. What is Virtual Reality?
A lot of people use the term “virtual reality” for different types of “Immersive Experiences”. This includes augmented and mixed reality as well as 360° video. Although they each offer alternate or altered reality experiences, they are quite different and too frequently are the technologies confused with one another.
- Virtual Reality
- Augmented Reality
- Mixed Reality
- 360° Video
In its simplest form, Virtual Reality (VR) transposes the user to an alternate world. The real world which the user is in, does not exist. This is done through live video or computer generated graphics and uses closed head-mounted displays (HMD’s) that completely blind the user from seeing anything in the real-world. The Oculus Rift, Playstation VR, HTC Vive, Google Daydream, Gear VR are examples of HMD’s.
A lot of people use the term “virtual reality” for different types of “Immersive Experiences”. This includes augmented and mixed reality as well as 360° video. Although they each offer alternate or altered reality experiences, they are quite different and too frequently are the technologies confused with one another.
- Virtual Reality
- Augmented Reality
- Mixed Reality
- 360° Video
In its simplest form, Virtual Reality (VR) transposes the user to an alternate world. The real world which the user is in, does not exist. This is done through live video or computer generated graphics and uses closed head-mounted displays (HMD’s) that completely blind the user from seeing anything in the real-world. The Oculus Rift, Playstation VR, HTC Vive, Google Daydream, Gear VR are examples of HMD’s.
Q 15. What is Non-Interactive VR?
With non-interactive VR applications and content, the user is a spectator in another world. They sit back and can look anywhere as if they were there. But they cannot interact (other than point and click). They are still fully immersed though and with added components such as immersive audio, the user is fully engulfed into a different reality thus altering the user’s senses, etc.
Types of Non-Interactive VR:
Experience — These are experiences which allow the user to feel actively involved and engaged but still in an entirely passive role.
Examples of Experience VR: Oculus Dreamdeck, G2A Land, Face Your Fears, Everest VR
Storytelling and Story Enabling — Examples are movies, short stories and narrative pieces. This is another important subject regarding the art of storytelling vs. story enabling with VR. Both deal with a certain plot the author has introduced, but while storytelling gives no control to the user, story enabling allows the user to interact with the story; thus giving them choices and some amounts of freedom to engage.
It is argued that this type of “VR Cinema” is yet to be discovered because current storytellers are unable to see beyond conventional cinematic processes which dictate every part of how the story is told. Creators of cinema content for the virtual realm are yet to be born.
With non-interactive VR applications and content, the user is a spectator in another world. They sit back and can look anywhere as if they were there. But they cannot interact (other than point and click). They are still fully immersed though and with added components such as immersive audio, the user is fully engulfed into a different reality thus altering the user’s senses, etc.
Types of Non-Interactive VR:
Experience — These are experiences which allow the user to feel actively involved and engaged but still in an entirely passive role.
Examples of Experience VR: Oculus Dreamdeck, G2A Land, Face Your Fears, Everest VR
Storytelling and Story Enabling — Examples are movies, short stories and narrative pieces. This is another important subject regarding the art of storytelling vs. story enabling with VR. Both deal with a certain plot the author has introduced, but while storytelling gives no control to the user, story enabling allows the user to interact with the story; thus giving them choices and some amounts of freedom to engage.
It is argued that this type of “VR Cinema” is yet to be discovered because current storytellers are unable to see beyond conventional cinematic processes which dictate every part of how the story is told. Creators of cinema content for the virtual realm are yet to be born.
Q 16. What is Interactive VR?
- This type of experience gives the user interactive abilities while in their alternate world. Users can fully immerse themselves in their alternate realities by moving forward or backwards, sideways, up and down. This immersion expands the user’s senses and they can also interact with objects by holding, throwing, pushing and pulling.
- Most of this is not real-world but instead computer generated using high powered game engine PC’s that allow for real time rendering.
- This type of experience gives the user interactive abilities while in their alternate world. Users can fully immerse themselves in their alternate realities by moving forward or backwards, sideways, up and down. This immersion expands the user’s senses and they can also interact with objects by holding, throwing, pushing and pulling.
- Most of this is not real-world but instead computer generated using high powered game engine PC’s that allow for real time rendering.
Q 17. What is Augmented Reality?
- This adds to our reality. It supplements the real world with digital objects. It does not take us elsewhere but instead enhances our present. It literally “augments” our reality instead of blocking out the world.
- With AR, computer generated graphics overlay the current reality and provide enhancing data that can be used regularly in day-to-day life. Examples of AR have been seen in movies for quite some time such as The Terminator, Minority Report and others.
- The digital object overlays can be text data, 3D objects or video such as with Google Glass notifications or on the head-up displays (HUD) in cars which provide valuable information to a driver.
- As Tim Cook, CEO of Apple said, “AR allows individuals to be present in the world but hopefully allows an improvement on what’s happening presently”
- This adds to our reality. It supplements the real world with digital objects. It does not take us elsewhere but instead enhances our present. It literally “augments” our reality instead of blocking out the world.
- With AR, computer generated graphics overlay the current reality and provide enhancing data that can be used regularly in day-to-day life. Examples of AR have been seen in movies for quite some time such as The Terminator, Minority Report and others.
- The digital object overlays can be text data, 3D objects or video such as with Google Glass notifications or on the head-up displays (HUD) in cars which provide valuable information to a driver.
- As Tim Cook, CEO of Apple said, “AR allows individuals to be present in the world but hopefully allows an improvement on what’s happening presently”
Q 18. What is Mixed Reality?
- MR is a mixture of VR and AR where virtual objects interact with real world objects. An example would be if you placed a virtual object (a cup for example) onto a real-world object (a table). The cup would remain in that same position as you walk or change locations. Basically, the virtual object attaches itself to the real-world object and it becomes part the real-world. Take a look at the Magic Beans demo or Bridge Engine Demo for awesome examples.
- Examples of Mixed Reality: Microsoft HoloLens, ODG headsets, Google Glass, Magic Beans Demo
- MR is a mixture of VR and AR where virtual objects interact with real world objects. An example would be if you placed a virtual object (a cup for example) onto a real-world object (a table). The cup would remain in that same position as you walk or change locations. Basically, the virtual object attaches itself to the real-world object and it becomes part the real-world. Take a look at the Magic Beans demo or Bridge Engine Demo for awesome examples.
- Examples of Mixed Reality: Microsoft HoloLens, ODG headsets, Google Glass, Magic Beans Demo
Q 19. What is 360° Content?
- 360° content can be easily created using the plethora of 360° cameras on the market today. Typically, this is a 2 step process where multiple cameras or lenses capture an image from a different angle and are then stitched together to create a single image that can be projected into a 360° environment. There are many challenges in filming and stitching 360° video that will be discussed in a later article.
- 360° content utilizes “live” video, or even pre-rendered computer generated graphics. It can be of concerts, car rides, drone videos, and so much more.
- 360° content can be easily created using the plethora of 360° cameras on the market today. Typically, this is a 2 step process where multiple cameras or lenses capture an image from a different angle and are then stitched together to create a single image that can be projected into a 360° environment. There are many challenges in filming and stitching 360° video that will be discussed in a later article.
- 360° content utilizes “live” video, or even pre-rendered computer generated graphics. It can be of concerts, car rides, drone videos, and so much more.
Q 20. Is 360° content VR?
No. This isn’t VR.
Reasons:-
- True VR utilizes sensors to track your head movements giving you the illusion that you are in this alternate world. When your head moves, the view of the world moves as well, affecting both your subconscious and conscious mind. It also tracks your position in space and requires highly powered computers with head-mounted displays such as the Rift, Vive or PS VR to give precise displays of individual frames that accurately match the head’s position.
- With 360° content, you are not fully immersed. You can look up, down and around but you can’t move forward. And frame rates are no where near in comparison therefore not tricking your brain into really believing you are in another world.
- 360° content at its most basic can be viewed without a headset on applications such as YouTube, Facebook posts or through websites requiring mouse movements to navigate.
No. This isn’t VR.
Reasons:-
- True VR utilizes sensors to track your head movements giving you the illusion that you are in this alternate world. When your head moves, the view of the world moves as well, affecting both your subconscious and conscious mind. It also tracks your position in space and requires highly powered computers with head-mounted displays such as the Rift, Vive or PS VR to give precise displays of individual frames that accurately match the head’s position.
- With 360° content, you are not fully immersed. You can look up, down and around but you can’t move forward. And frame rates are no where near in comparison therefore not tricking your brain into really believing you are in another world.
- 360° content at its most basic can be viewed without a headset on applications such as YouTube, Facebook posts or through websites requiring mouse movements to navigate.
Q 21. Write queries to declare the primary key and foreign key for the same table.
CREATE TABLE location(
location_id varchar(10) NOT NULL,
location varchar(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(location_id),
FOREIGN KEY(location) REFERENCES detail(location));
location_id varchar(10) NOT NULL,
location varchar(40) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(location_id), FOREIGN KEY(location) REFERENCES detail(location));
Q 22. Difference between Having and Where Clause.
| Where | Having |
|---|---|
| WHERE clause is used to filter records from the table depending on criteria. | The HAVING Clause is used to filter records from groups depending on the condition that is given. |
| Can be used without “groupby” clause | Can’t be used without “groupby” clause |
| Implemented in row operations | Implemented in Column operations |
| Where | Having |
|---|---|
| WHERE clause is used to filter records from the table depending on criteria. | The HAVING Clause is used to filter records from groups depending on the condition that is given. |
| Can be used without “groupby” clause | Can’t be used without “groupby” clause |
| Implemented in row operations | Implemented in Column operations |
Q 23. Explain the difference between Drop, Truncate and Delete.
|
Drop |
Truncate |
Delete |
|---|---|---|
| A Data Definition Language (DDL) command is DROP. A table is dropped from the database using the DROP command. | TRUNCATE is a DDL command (Data Definition Language). TRUNCATE is run with a table lock, which locks the entire table in order to erase all records. | DELETE is a command in the Data Manipulation Language (DML). DELETE uses a row lock mechanism, which locks each row in the table for deletion. |
| Syntax: DROP TABLE table_name | Syntax: TRUNCATE TABLE table_name | Syntax: DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition |
| No rollback is possible. | It's possible to revert. | There is no way back return is conceivable |
|
Drop |
Truncate |
Delete |
|---|---|---|
| A Data Definition Language (DDL) command is DROP. A table is dropped from the database using the DROP command. | TRUNCATE is a DDL command (Data Definition Language). TRUNCATE is run with a table lock, which locks the entire table in order to erase all records. | DELETE is a command in the Data Manipulation Language (DML). DELETE uses a row lock mechanism, which locks each row in the table for deletion. |
| Syntax: DROP TABLE table_name | Syntax: TRUNCATE TABLE table_name | Syntax: DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition |
| No rollback is possible. | It’s possible to revert. | There is no way back return is conceivable |
Q 24. What is Dynamic programming?
Dynamic Programming is a computer programming technique that aids in the effective solution of issues with overlapping subproblems and optimal substructure properties.
Q 25. What happens after you enter the URL of a website?
After you type a URL in a web browser, the domain name is resolved to an IP address by the browser via DNS. An HTTP request is made to the server by the browser. An HTTP response is returned by the server.
Q 26. What is R? What are its advantages?
R is a statistical computing and graphics programming language that you may use to clean, analyze, and graph your data. It is frequently used by statisticians and research techniques lecturers, as well as researchers from several fields, to estimate and display results.
Advantages of R are given below:
- Open source programming language.
- R is a platform-independent programming language that can perform a variety of machine learning tasks.
- R enables us to manipulate data.
- R makes graphing and charting easier.
- It has a lot of different bundles.
- A programming language that is always changing.
Advantages of R are given below:
1. Open source programming language.
2. R is a platform-independent programming language that can perform a variety of machine learning tasks.
3.R enables us to manipulate data.
4. R makes graphing and charting easier
It has a lot of different bundles.
A programming language that is always changing.
Q 27. Difference between call by value and call by reference.
| Call by value | Call by reference |
|---|---|
| We pass variable values to a function when we call it. “Call By Values” functions are what they’re called. | Instead of giving the values of variables to a function, we pass the address of variables (location of variables) to the “Call By References” function. |
| The value of each variable in the calling function is transferred into the called function’s corresponding fake variables in this technique. | The addresses of genuine variables in the calling code are copied into dummy variables in the called function using this procedure. |
| Simple approach is used to pass variable values. | To hold the address values of variables, pointer variables must be defined. |
| We can’t change the values of actual variables through function calls in the call by values. | Through function calls, we can change the values of variables in the call by reference. |
| Call by value | Call by reference |
|---|---|
| We pass variable values to a function when we call it. "Call By Values" functions are what they're called. | Instead of giving the values of variables to a function, we pass the address of variables (location of variables) to the "Call By References" function. |
| The value of each variable in the calling function is transferred into the called function's corresponding fake variables in this technique. | The addresses of genuine variables in the calling code are copied into dummy variables in the called function using this procedure. |
| Simple approach is used to pass variable values. | To hold the address values of variables, pointer variables must be defined. |
| We can't change the values of actual variables through function calls in the call by values. | Through function calls, we can change the values of variables in the call by reference. |
Q 28. What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a network of peer-to-peer nodes that keeps transactional records, also known as blocks, of the public in various databases, also known as the “chain.” This type of storage is sometimes referred to as a “digital ledger.”
Q 29. What is the difference between Blockchain and Bitcoin?
Blockchain is the technology that powers the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, although it is not the only distributed ledger system based on blockchain technology. Other cryptocurrencies have their own blockchain and distributed ledger designs.
Q 30. What is Big Data Analytics?
Big data analytics is the use of advanced analytic techniques to very large, heterogeneous data sets, which can contain structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, as well as data from many sources and sizes ranging from terabytes to zettabytes.
Q 31. Explain Exception Handling with an example.
When an unexpected event occurs that needs special processing, an exception arises. a user providing abnormal input, a file system error being encountered when trying to read or write a file, or a program attempting to divide by zero are examples.
Q 32. What is the use of the “finally” block in exception handling?
Finally, the try keyword specifies a block of code that we employ. It specifies code that is always executed after the try and catch blocks, but before the method is finished. Regardless of whether an exception is thrown or caught, the finally block runs.
Q 33. Difference between JDK and JRE.
|
JDK |
JRE |
|---|---|
| JDK stands for Java Development Kit | JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. |
| It’s a programming environment for creating Java apps and applets. | It is a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) implementation that is specifically designed to offer an environment in which Java programs may be executed. |
|
JDK |
JRE |
|---|---|
| JDK stands for Java Development Kit | JRE stands for Java Runtime Environment. |
| It's a programming environment for creating Java apps and applets. | It is a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) implementation that is specifically designed to offer an environment in which Java programs may be executed. |
Q 34. What is JVM?
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is a machine that’s abstract. It is a standard that offers a runtime environment for executing Java bytecode.
Q 35. Why does JAVA not support multiple inheritance?
This is done in order to avoid ambiguity. Consider the following scenario: class B extends classes A and C, and both classes A and C have the same method show (). The java compiler is now unable to determine which display method it should inherit. Multiple inheritances are not permitted in Java to avoid such a problem.
Q 36. Why JAVA does not support pointers?
Java does not employ pointers because they provide direct access to the memory region, which is a security risk. At runtime, pointers use a lot of memory. Java does not support pointers in order to save memory space.
Q 37. What is a Static variable and method in Java?
The static variable is a class-level variable that is shared by all class objects, i.e. there is only one copy of the static variable shared by all class objects. A static method manipulates a class’s static variables.
Q 38. Can you overload the main method in java?
Yes. Although we may override the main method in Java, the JVM will only invoke the original main method, never our overloaded main method.
Q 39. What is Throwable class?
Throwable class is the superclass of all errors and exceptions. The Java Virtual Machine or the Java throw command can only toss objects that are instances of this class (or one of its subclasses).
Q 40. What are transactions in databases?
In the context of a database, a transaction is a logical unit that is processed separately for data retrieval or modifications. A database transaction is defined by experts as a “unit of work” completed within a database design environment.
Also Check:

Technical Interview Dashboard
Visit our Technical Interview Dashboard for to get the most asked Technical Interview Question and Answers, including Top C Interview Questions, Top JAVA Interview Questions and More

TCS Digtial Interview Experience
Read Interview Experiences of candidates who got placed in TCS from the 2021-22 batch. Fins out how they prepared, what questions are asked in TCS Interview and more
(Use Coupon Code “CT10″ and get 10% off and additional months)


 Apply For Jobs
Apply For Jobs Get Hiring Updates
Get Hiring Updates



Login/Signup to comment